The lowest unit of symbolic representation. More...
#include <basic.h>
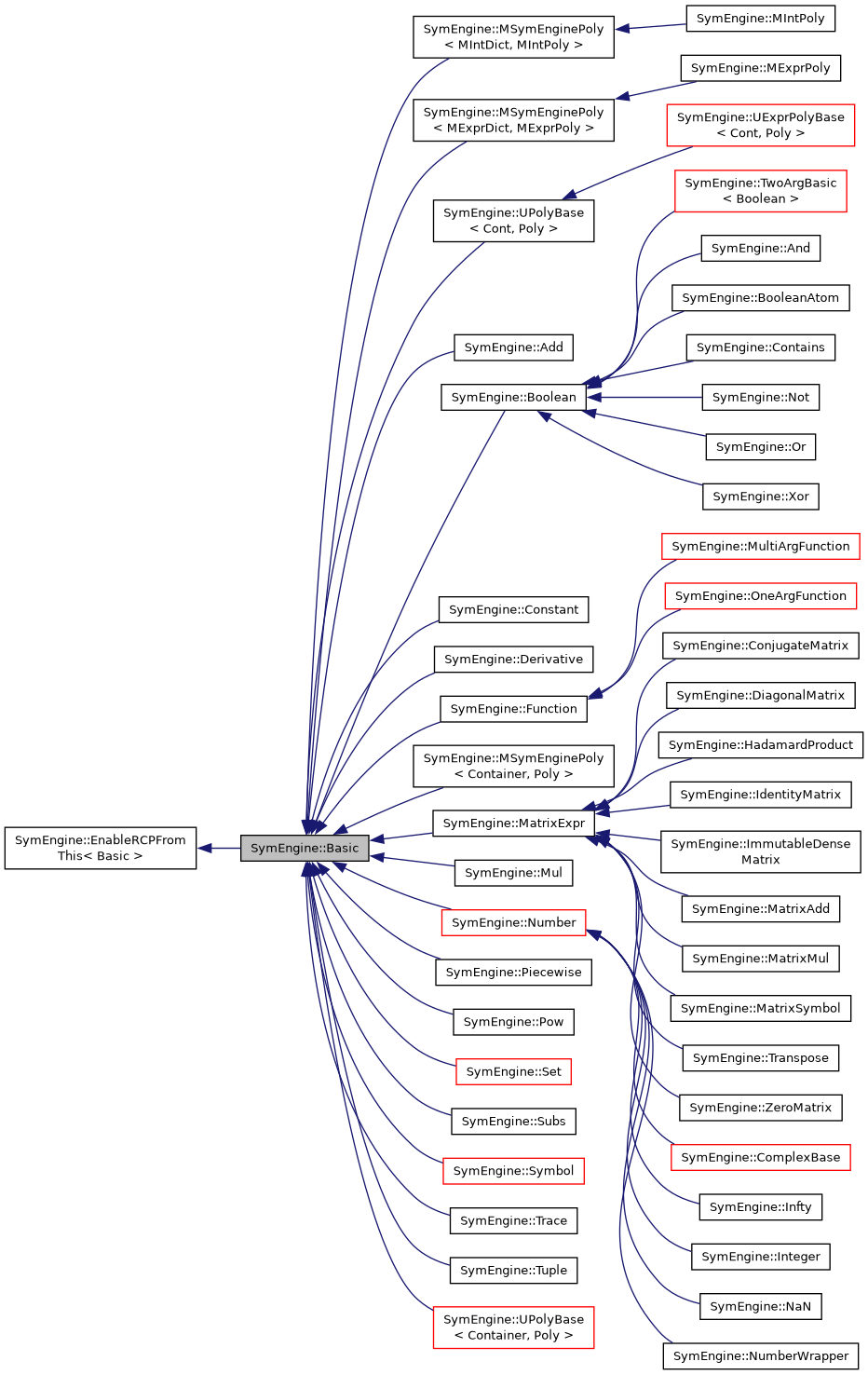
 Inheritance diagram for SymEngine::Basic:
Inheritance diagram for SymEngine::Basic: Collaboration diagram for SymEngine::Basic:
Collaboration diagram for SymEngine::Basic:Public Member Functions | |
| TypeID | get_type_code () const |
| Basic () | |
| Constructor. | |
| Basic (const Basic &)=delete | |
| Delete the copy constructor and assignment. | |
| Basic & | operator= (const Basic &)=delete |
| Assignment operator in continuation with above. | |
| Basic (Basic &&)=delete | |
| Delete the move constructor and assignment. | |
| Basic & | operator= (Basic &&)=delete |
| Assignment operator in continuation with above. | |
| virtual hash_t | __hash__ () const =0 |
| hash_t | hash () const |
| virtual bool | __eq__ (const Basic &o) const =0 |
| Test equality. More... | |
| bool | __neq__ (const Basic &o) const |
true if this is not equal to o. More... | |
| int | __cmp__ (const Basic &o) const |
| Comparison operator. | |
| virtual int | compare (const Basic &o) const =0 |
| std::string | __str__ () const |
| std::string | dumps () const |
| Returns a string of the instance serialized. | |
| RCP< const Basic > | subs (const map_basic_basic &subs_dict) const |
| Substitutes 'subs_dict' into 'self'. | |
| RCP< const Basic > | xreplace (const map_basic_basic &subs_dict) const |
| virtual RCP< const Basic > | expand_as_exp () const |
| expands the special function in terms of exp function | |
| virtual vec_basic | get_args () const =0 |
| Returns the list of arguments. | |
| virtual void | accept (Visitor &v) const =0 |
| virtual void | accept (EvalRealDoubleVisitorFinal &v) const =0 |
| RCP< const Basic > | diff (const RCP< const Symbol > &x, bool cache=true) const |
 Public Member Functions inherited from SymEngine::EnableRCPFromThis< Basic > Public Member Functions inherited from SymEngine::EnableRCPFromThis< Basic > | |
| RCP< Basic > | rcp_from_this () |
| Get RCP<T> pointer to self (it will cast the pointer to T) | |
| RCP< const Basic > | rcp_from_this () const |
| Get RCP<const T> pointer to self (it will cast the pointer to const T) | |
| RCP< const T2 > | rcp_from_this_cast () const |
| Get RCP<T2> pointer to self (it will cast the pointer to T2) | |
| unsigned int | use_count () const |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static RCP< const Basic > | loads (const std::string &) |
| Creates an instance of a serialized string. | |
Data Fields | |
| TypeID | type_code_ |
Private Attributes | |
| hash_t | hash_ |
| Private variables. | |
Detailed Description
The lowest unit of symbolic representation.
Classes like Add, Mul, Pow are initialized through their constructor using their internal representation. Add, Mul have a 'coeff' and 'dict', while Pow has 'base' and 'exp'. There are restrictions on what 'coeff' and 'dict' can be (for example 'coeff' cannot be zero in Mul, and if Mul is used inside Add, then Mul's coeff must be one, etc.). All these restrictions are checked when WITH_SYMENGINE_ASSERT is enabled inside the constructors using the is_canonical() method. That way, you don't have to worry about creating Add / Mul / Pow with wrong arguments, as it will be caught by the tests. In the Release mode no checks are done, so you can construct Add / Mul / Pow very quickly. The idea is that depending on the algorithm, you sometimes know that things are already canonical, so you simply pass it directly to the constructors of the Basic classes and you avoid expensive type checking and canonicalization. At the same time, you need to make sure that tests are still running with WITH_SYMENGINE_ASSERT enabled, so that the Basic classes are never in an inconsistent state.
Summary: always try to construct the expressions Add / Mul / Pow directly using their constructors and all the knowledge that you have for the given algorithm, that way things will be very fast. If you want slower but simpler code, you can use the add(), mul(), pow() functions that peform general and possibly slow canonicalization first.
- Note
- Any
Basicclass can be used in a "dictionary", due to the methods:__hash__() __eq__(o)
- Warning
- Subclasses must implement
__hash__()and__eq__()
Member Function Documentation
◆ __eq__()
|
pure virtual |
Test equality.
A virtual function for testing the equality of two Basic objects
- Deprecated:
- Use eq(const Basic &a, const Basic &b) non-member method
- Parameters
-
o a constant reference to object to test against
- Returns
- True if
thisis equal too
Implemented in SymEngine::Tuple, SymEngine::Dummy, SymEngine::Symbol, SymEngine::ImageSet, SymEngine::ConditionSet, SymEngine::Complement, SymEngine::Intersection, SymEngine::Union, SymEngine::Naturals0, SymEngine::Naturals, SymEngine::Integers, SymEngine::Rationals, SymEngine::Reals, SymEngine::Complexes, SymEngine::Interval, SymEngine::FiniteSet, SymEngine::UniversalSet, SymEngine::EmptySet, SymEngine::SeriesBase< Poly, Coeff, Series >, SymEngine::SeriesBase< UExprDict, Expression, UnivariateSeries >, SymEngine::RealDouble, SymEngine::Rational, SymEngine::Pow, SymEngine::UPolyBase< Container, Poly >, SymEngine::UPolyBase< Cont, Poly >, SymEngine::MSymEnginePoly< Container, Poly >, SymEngine::MSymEnginePoly< MIntDict, MIntPoly >, SymEngine::MSymEnginePoly< MExprDict, MExprPoly >, SymEngine::NaN, SymEngine::Mul, SymEngine::ZeroMatrix, SymEngine::Transpose, SymEngine::Trace, SymEngine::MatrixSymbol, SymEngine::MatrixMul, SymEngine::MatrixAdd, SymEngine::ImmutableDenseMatrix, SymEngine::IdentityMatrix, SymEngine::HadamardProduct, SymEngine::DiagonalMatrix, SymEngine::ConjugateMatrix, SymEngine::Xor, SymEngine::Not, SymEngine::Or, SymEngine::And, SymEngine::Piecewise, SymEngine::Contains, SymEngine::BooleanAtom, SymEngine::Integer, SymEngine::Infty, SymEngine::Subs, SymEngine::Derivative, SymEngine::FunctionSymbol, SymEngine::MultiArgFunction, SymEngine::TwoArgBasic< Boolean >, SymEngine::OneArgFunction, SymEngine::Constant, SymEngine::ComplexDouble, SymEngine::Complex, and SymEngine::Add.
◆ __hash__()
|
pure virtual |
Calculates the hash of the given SymEngine class. Use Basic.hash() which gives a cached version of the hash.
- Returns
- 64-bit integer value for the hash
Implemented in SymEngine::UPolyBase< Container, Poly >, SymEngine::UPolyBase< Cont, Poly >, SymEngine::Tuple, SymEngine::Dummy, SymEngine::Symbol, SymEngine::ImageSet, SymEngine::ConditionSet, SymEngine::Complement, SymEngine::Intersection, SymEngine::Union, SymEngine::Naturals0, SymEngine::Naturals, SymEngine::Integers, SymEngine::Rationals, SymEngine::Reals, SymEngine::Complexes, SymEngine::Interval, SymEngine::FiniteSet, SymEngine::UniversalSet, SymEngine::EmptySet, SymEngine::UnivariateSeries, SymEngine::RealDouble, SymEngine::Rational, SymEngine::Pow, SymEngine::URatPoly, SymEngine::UIntPoly, SymEngine::UExprPoly, SymEngine::MExprPoly, SymEngine::MIntPoly, SymEngine::NaN, SymEngine::Mul, SymEngine::ZeroMatrix, SymEngine::Transpose, SymEngine::Trace, SymEngine::MatrixSymbol, SymEngine::MatrixMul, SymEngine::MatrixAdd, SymEngine::ImmutableDenseMatrix, SymEngine::IdentityMatrix, SymEngine::HadamardProduct, SymEngine::DiagonalMatrix, SymEngine::ConjugateMatrix, SymEngine::Xor, SymEngine::Not, SymEngine::Or, SymEngine::And, SymEngine::Piecewise, SymEngine::Contains, SymEngine::BooleanAtom, SymEngine::Integer, SymEngine::Infty, SymEngine::Subs, SymEngine::Derivative, SymEngine::FunctionSymbol, SymEngine::MultiArgFunction, SymEngine::TwoArgBasic< Boolean >, SymEngine::OneArgFunction, SymEngine::GaloisField, SymEngine::Constant, SymEngine::ComplexDouble, SymEngine::Complex, and SymEngine::Add.
◆ __neq__()
|
inline |
true if this is not equal to o.
- Returns
- true if not equal
Definition at line 15 of file basic-inl.h.
◆ __str__()
| std::string SymEngine::Basic::__str__ | ( | ) | const |
◆ compare()
|
pure virtual |
Returns -1, 0, 1 for this < o, this == o, this > o. This method is used when you want to sort things like x+y+z into canonical order. This function assumes that o is the same type as this. Use __cmp__ if you want general comparison.
Implemented in SymEngine::UPolyBase< Container, Poly >, SymEngine::UPolyBase< Cont, Poly >, SymEngine::Tuple, SymEngine::Dummy, SymEngine::Symbol, SymEngine::ImageSet, SymEngine::ConditionSet, SymEngine::Complement, SymEngine::Intersection, SymEngine::Union, SymEngine::Naturals0, SymEngine::Naturals, SymEngine::Integers, SymEngine::Rationals, SymEngine::Reals, SymEngine::Complexes, SymEngine::Interval, SymEngine::FiniteSet, SymEngine::UniversalSet, SymEngine::EmptySet, SymEngine::UnivariateSeries, SymEngine::RealDouble, SymEngine::Rational, SymEngine::Pow, SymEngine::MSymEnginePoly< Container, Poly >, SymEngine::MSymEnginePoly< MIntDict, MIntPoly >, SymEngine::MSymEnginePoly< MExprDict, MExprPoly >, SymEngine::NaN, SymEngine::Mul, SymEngine::ZeroMatrix, SymEngine::Transpose, SymEngine::Trace, SymEngine::MatrixSymbol, SymEngine::MatrixMul, SymEngine::MatrixAdd, SymEngine::ImmutableDenseMatrix, SymEngine::IdentityMatrix, SymEngine::HadamardProduct, SymEngine::DiagonalMatrix, SymEngine::ConjugateMatrix, SymEngine::Xor, SymEngine::Not, SymEngine::Or, SymEngine::And, SymEngine::Piecewise, SymEngine::Contains, SymEngine::BooleanAtom, SymEngine::Integer, SymEngine::Infty, SymEngine::Subs, SymEngine::Derivative, SymEngine::FunctionSymbol, SymEngine::MultiArgFunction, SymEngine::TwoArgBasic< Boolean >, SymEngine::OneArgFunction, SymEngine::GaloisField, SymEngine::Constant, SymEngine::ComplexDouble, SymEngine::Complex, and SymEngine::Add.
◆ hash()
|
inline |
Returns the hash of the SymEngine class: This method caches the value
Use std::hash to get the hash. Example:
RCP<const Symbol> x = symbol("x");
std::hash<Basic> hash_fn;
std::cout << hash_fn(*x);
- Returns
- 64-bit integer value for the hash
Definition at line 7 of file basic-inl.h.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- /home/runner/work/symengine/symengine/symengine/basic.h
- /home/runner/work/symengine/symengine/symengine/basic-inl.h
- /home/runner/work/symengine/symengine/symengine/basic.cpp
- /home/runner/work/symengine/symengine/symengine/derivative.cpp